 Discovery Information Discovery Information
|
| Who: Louis Vauquelin |
| When: 1797 |
| Where: France |
|
 Name Origin Name Origin
|
| Greek: chroma (colour). Due to the many colourful compounds that can be made from it.
|
| "Chromium" in different languages. |
|
 Sources Sources
|
| Does not occur free in nature. Chromite [Fe,Mg(CrO4)] is its most important mineral. Chromium ores are mined today in South Africa, Zimbabwe, Finland, India, Kazakihstan and the Philippines.
|
| Worldwide production in 2006 was 19.2 million tons. Reserves are estimated at over 1 billion tonnes. |
|
 Abundance Abundance
|
| Universe: 15 ppm (by weight) |
| Sun: 20 ppm (by weight) |
| Carbonaceous meteorite: 3100 ppm |
| Earth's Crust: 100 ppm |
| Seawater: |
| Atlantic surface: 1.8 x 10-4 ppm
|
| Atlantic deep: 2.3 x 10-4 ppm
|
| Pacific surface: 1.5 x 10-4 ppm
|
| Pacific deep: 2.5 x 10-4 ppm
|
| Human: |
| 30 ppb by weight |
| 4 ppb by atoms |
|
 Uses Uses
|
| Used to make stainless steel. Also used in plating for car parts, magnetic tape, tools, knives, camouflage paint, stereos,
and lasers. It gives rubies and emeralds their colour.
|
| Chromium(VI) oxide (CrO3) is used to manufacture magnetic tape, where its higher coercivity than iron oxide tapes gives better performance.
|
|
 History History
|
| On 26th July 1761, Johann Gottlob Lehmann found an orange-red mineral in the Ural Mountains which he named Siberian red lead.
Though misidentified as a lead compound with selenium and iron components, the material was in fact lead chromate with a formula of PbCrO4, now known as the mineral crocoite (PbCrO4).
|
| In 1770, Peter Simon Pallas visited the same site as Lehmann and found a red "lead" mineral that had very useful properties
as a pigment in paints. The use of Siberian red lead as a paint pigment developed rapidly. A bright yellow made from crocoite
became a colour in fashion.
|
| In 1797, Louis Nicolas Vauquelin received samples of crocoite ore. He was able to produce chromium oxide with a chemical formula of CrO3, by mixing crocoite with hydrochloric acid. In 1798, Vauquelin discovered that he could isolate metallic chromium by heating the oxide in a charcoal oven. He was also able to detect traces
of chromium in precious gemstones, such as ruby, or emerald. Later this year he successfully isolated chromium atoms.
|
| During the 1800s chromium was primarily used as a component of paints and in tanning salts but now metal alloys account for
85% of the use of chromium. The remainder is used in the chemical industry and refractory and foundry industries.
|
|
|
 Hazards Hazards
|
| Chromium may act as a carcinogen when in powdered form. |
| Chromium metal and chromium(III) compounds are not usually considered health hazards, but hexavalent chromium (chromium VI) compounds can be toxic if orally ingested or inhaled. The lethal dose of poisonous chromium (VI) compounds is about one half teaspoon of material. Most chromium (VI) compounds are irritating to eyes, skin and mucous membranes. Chronic exposure to chromium (VI) compounds can cause permanent eye injury, unless properly treated. Chromium(VI) is an established human carcinogen.
|
| World Health Organization recommended maximum allowable concentration in drinking water for chromium (VI) is 0.05 milligrams
per liter.
|
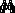
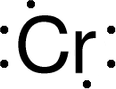
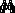
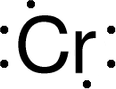
 Discovery Information
Discovery Information
 Name Origin
Name Origin
 Sources
Sources
 Abundance
Abundance
 Uses
Uses
 History
History
 Hazards
Hazards